√70以上 s p d f orbitals diagram 346291-What does s p d f orbitals stand for
2 how many electrons do the F orbitals holds total?The maximum number of electrons that p orbital can hold is 6 This is because one p orbital is composed of three sub orbitals named as p x, p y and p z Each of these orbitals can hold a maximum of 2 electrons d orbital These orbitals look like two dumbbells in the same plane However, it is a complicated 3D structure than s and p orbitalsThis means that the s,p,d,f electron configuration for Barium Barium, complete electron configuration Barium Full electron configuration of barium 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2 Oxidation States, 2 Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 18 8 2 Electron Configuration, Xe 6s2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2

Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry
What does s p d f orbitals stand for
What does s p d f orbitals stand for-Shapes of sorbitals The sorbitals are spherically symmetrical about the nucleus It implies that, p subshell have three orbitals called as p x, p y and p z Shape of porbitals We have three porbitals, commonly known as p x, p y and p z These three porbitals, possesses equivalent energy and therefore, have same relation with thenucleusP orbital having 3 orbitals hence max no of electrons 6 d orbital having 5 orbitals hence max no of electrons 10 F orbital having 7 orbitals hence max no of electrons 14 the outer orbit having S and P orbitals , 8 electrons or valence electrons present coefficients are nothingbut orbit or shell no


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
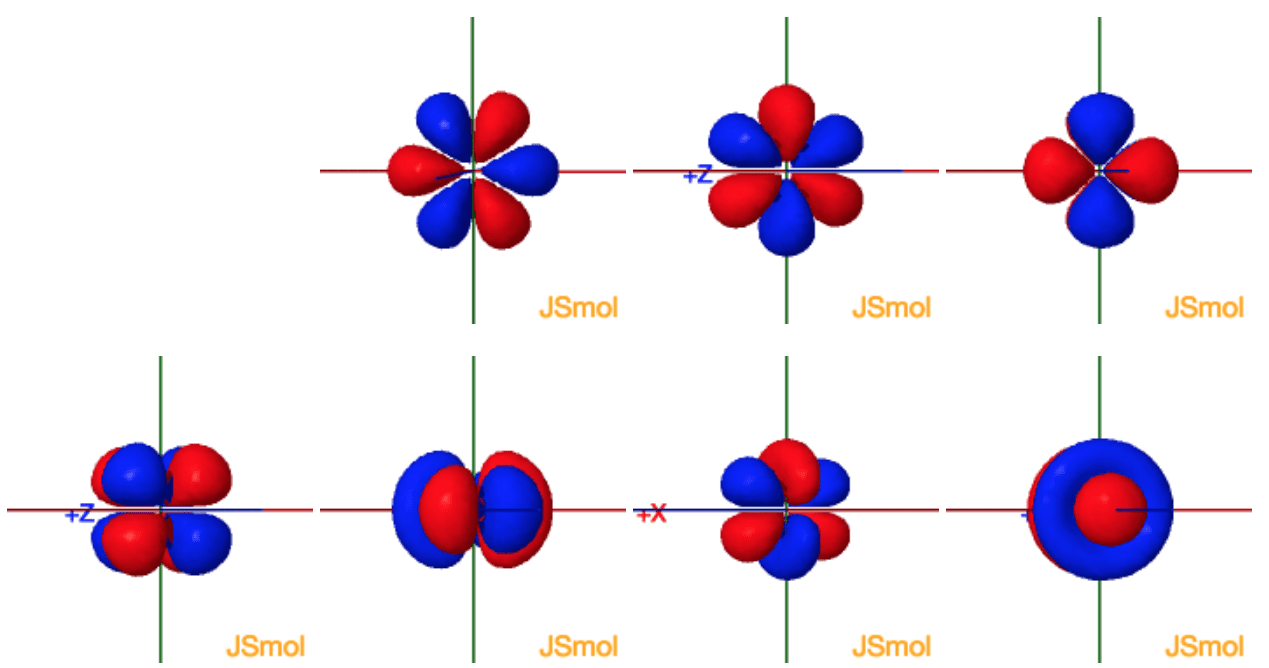
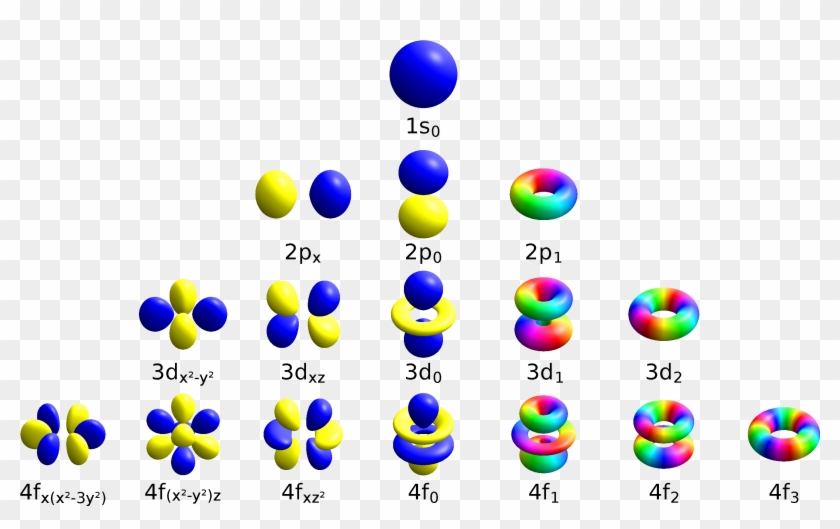
An sorbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a porbitals is dumbbellshaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped The fifth d orbital is shaped like an elongated dumbbell with a doughnut around its middle The orbitals in an atom are organized into different layers or electron shellsShapes of Orbitals and Electron Density Patterns The s orbitals are spherical, while p orbitals are polar and oriented in particular directions (x, y, and z) It may be simpler to think of these two letters in terms of orbital shapes (d and f aren't described as readily)However, if you look at a crosssection of an orbital, it isn't uniformExplanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram Orbitals in the 2p sublevel are degenerate orbitals – Which means that the 2px, 2py, and 2pz orbitals have the exact same energy, as illustrated in the diagram provided below Similarly, the 3px, 3py, and 3pz are degenerate orbitals
The empty f orbitals in lanthanum, actinium, and thorium contribute to chemical bonding, as do the empty p orbitals in transition metals 32 Vacant s, d, and f orbitals have been shown explicitly, as is occasionally done, 33 to emphasise the filling order and to clarify that even orbitals unoccupied in the ground state (eg lanthanum 4f orFigure 5 Boundary surface diagrams of the seven f orbitals Degenerate Orbitals Degenerate orbitals are orbitals having the same energy These orbital are different (may have a different orientation in space around the atomic nucleus) but possess the same energy The degeneracy of p orbital remains unaffected in presence of external field butMaximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitals Maximum 14 electrons in 7 orbitals
For l = 1, the letter is s, for l = 2 it's p, for l = 3 it's d, for l = 4 it's f and for higher numbers it increases alphabetically from this point Remember that s orbitals contain a maximum of two electrons, p orbitals a maximum of six, d a maximum of 10 and f a maximum of 14In sp hybridization, the s orbital overlaps with only one p orbital Atoms that exhibit sp hybridization have sp orbitals that are linearly oriented;Each of the porbitals holds two electrons, for a total of six electrons in the porbitals According to Hund's Rule, each porbital per energy level must receive one electron before earning a second electron The pblock starts with the column containing boron and ends with the column of noble gases


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital
For example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one nodeD and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals that become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are nine total



What Is The Shape Of An F Orbital Quora



Solved Please Explain What All These Mdz Ns Pz Mean And Chegg Com
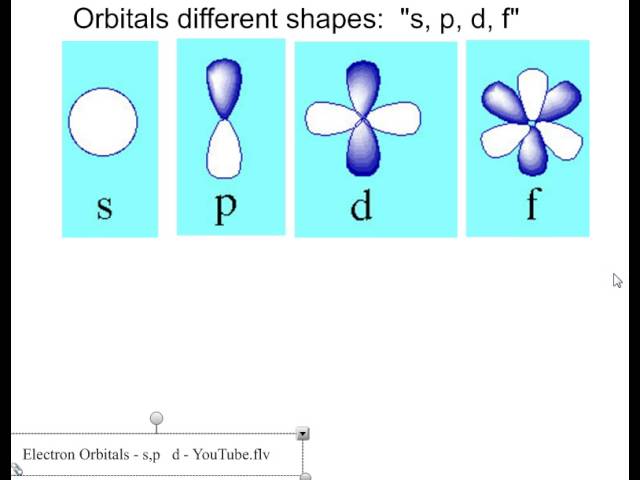
S, p, d, and f Orbitals The shapes corresponding to each orbital are designated by a single letter (chosen based on older analyses of atomic emission spectra) You must be able to draw the shape of an s and a p orbital The first orbital we will examine is the most basic orbital shape It is an s orbital32 Aufbau's diagram the order of filling of electrons in orbitals electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 4s2 3d6 orbital notation electron configuration Ø Ø Ø O that show electrons Hund's ruleThis means that the s,p,d,f electron configuration for Barium Barium, complete electron configuration Barium Full electron configuration of barium 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2 Oxidation States, 2 Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 18 8 2 Electron Configuration, Xe 6s2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 6s2



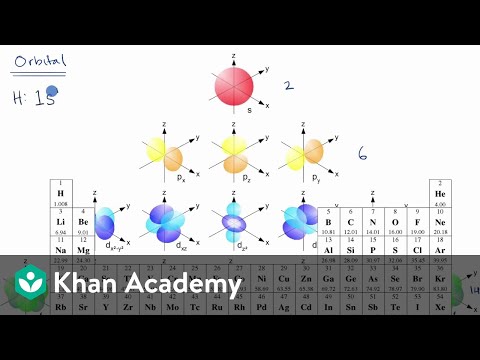
Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
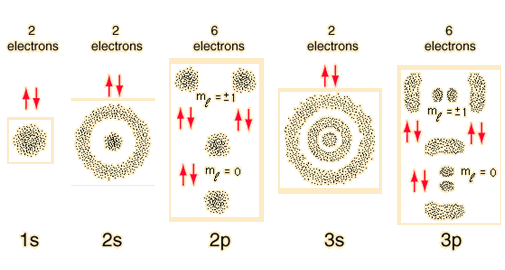
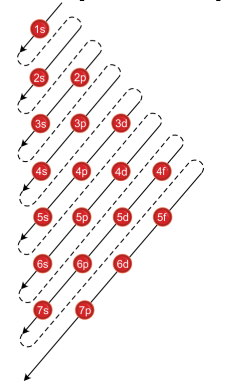
When we write the configuration we'll put all 26 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the Iron atom Video Fe, Fe 2, and Fe 3 Electron Configuration Notation In writing the electron configuration for Iron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Iron go in the 2sTwo sp orbitals will be at 180 degrees to each other Any central atom surrounded by just two regions of valence electron density in a molecule will exhibit sp hybridization Some examples include the mercury atom in the linear HgCl 2 moleculeThe diagram shows the number of subshell by using boxes or lines for electrons (use three for porbitals, five for dorbitals, and 7 for forbitals) In each box the spin of an electron is noted by using arrows, up arrows mean 1⁄2 spin and down arrows mean –1⁄2 spin For example, the orbital diagram for the first 18 atoms are shown below
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education
D and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are a total ofS P D F 4 types of orbitals in energy levels where are orbitals found?This version of The Orbitron is a partial rewrite of the 02 version of The Orbitron It is not finished there are still some missing images, missing videos, errors in orbital names, many typos, incorrect labels, no hybrid orbitals, and no molecular orbitals


Orbitals



Shapes Of Orbitlas And Electronic Configuration Class 11 Chemistry
The porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;The s orbital electron will be more tightly bound to the nucleus as compared to the p orbital electron, which is more tightly bound in regard to a d orbital electron for a given value of the principal quantum number As compared to p orbital electrons, s orbital electrons will have more negative or lesser amount of energy Here, the p orbitalMany real orbitals, such as 2s, 2p, and 3d orbitals have regions with both positive and negative phase These regions are separated by nodes For example, the diagrams below show 1s, 2s, and 3s orbitals Notice how the 2s and 3s orbitals have radial nodes separating different phases
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ShellAtomicModel-5a6ab592aded4bb7a1328f809e4f10da.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
F ORBITALS At the fourth and higher levels, there are seven f orbitals in addition to the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals Counting the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals, this makes a total of 16 orbitals in the fourth level They have even more complicated shapes s, p, d, and f orbitals are available at all higher energy levels as wellShapes of sorbitals The sorbitals are spherically symmetrical about the nucleus It implies that, p subshell have three orbitals called as p x, p y and p z Shape of porbitals We have three porbitals, commonly known as p x, p y and p z These three porbitals, possesses equivalent energy and therefore, have same relation with thenucleusFor l = 1, the letter is s, for l = 2 it's p, for l = 3 it's d, for l = 4 it's f and for higher numbers it increases alphabetically from this point Remember that s orbitals contain a maximum of two electrons, p orbitals a maximum of six, d a maximum of 10 and f a maximum of 14



How To Draw All 5 D Orbitals Quora



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange
D and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are a total ofThe shapes of p, d and forbitals are described verbally here and shown graphically in the Orbitals table below The three porbitals for n = 2 have the form of two ellipsoids with a point of tangency at the nucleus (the twolobed shape is sometimes referred to as a " dumbbell "—there are two lobes pointing in opposite directions from each other)For example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2


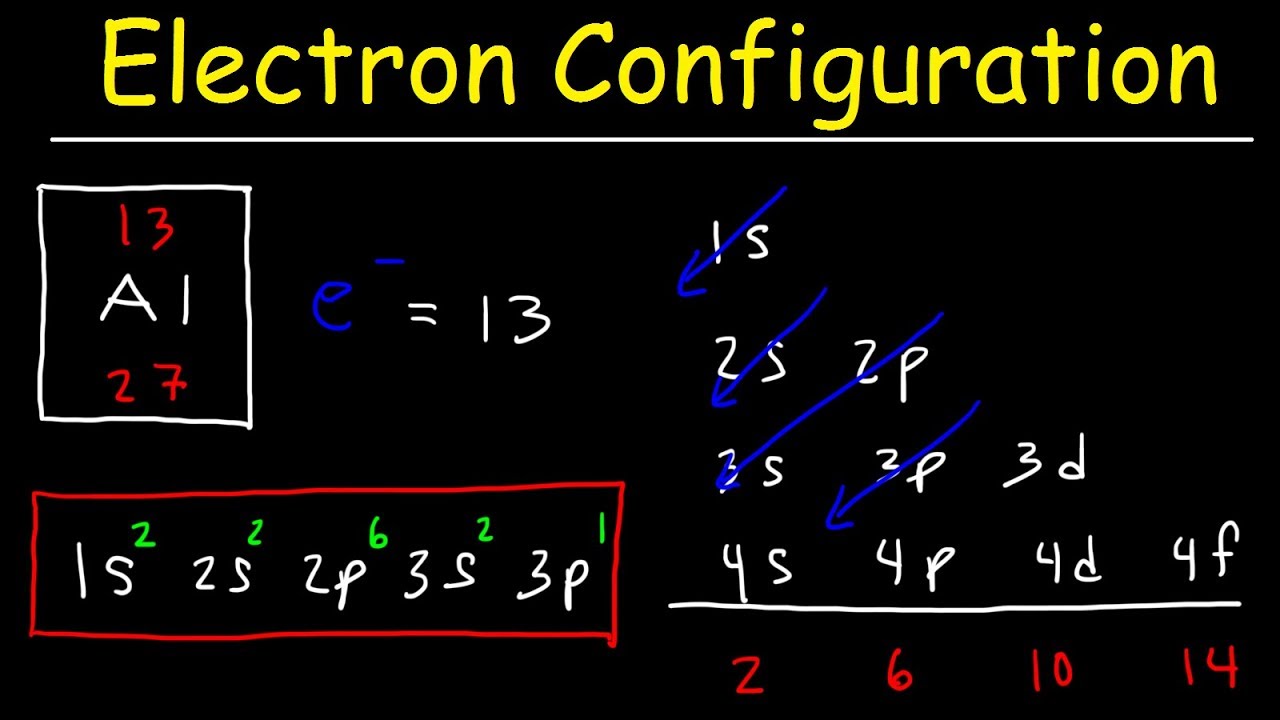
Electron Configurations



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Definition Examples Diagrams
Footnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellFootnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellAtomic Orbitals A Electron Location • Sublevel –Shape of electron cloud • s = spherical • p = dumbbell • d = too complex • f = too complex • 1st E level has 1 sublevel s • 2nd E level has 2 sublevels s and p • 3rd E level has 3 sublevels s, p, and d • 4th E level has 4 sublevels s, p, d and f


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model



Quantum Numbers N L Ml Ms Spdf Orbitals Youtube
The diagram shows the number of subshell by using boxes or lines for electrons (use three for porbitals, five for dorbitals, and 7 for forbitals) In each box the spin of an electron is noted by using arrows, up arrows mean 1⁄2 spin and down arrows mean –1⁄2 spin For example, the orbital diagram for the first 18 atoms are shown belowTwo sp orbitals will be at 180 degrees to each other Any central atom surrounded by just two regions of valence electron density in a molecule will exhibit sp hybridization Some examples include the mercury atom in the linear HgCl 2 moleculeQuantum Numbers Orbital Diagram Quantum numbers set like principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum number and fine structure of electromagnetic spectrum lines of atoms in mechanics define the electron energy levels and shapes diagram of s, p, dorbital, or orbitals in physics and chemistryBohr's theory of hydrogen spectrum and Sommerfeld theory met with number of difficulties when



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


Figure A 1 Angular Dependence Of The S P D And F Orbitals With L Download Scientific Diagram
The porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;Like sorbitals, porbitals also increase in size with the increase in value of n The boundary surface diagrams of ls, 2p x, 2p y and 2p z orbitals are shown in Fig 524 Fig 524 The boundary surface diagrams of 1 s and 2p orbitals The five dorbitals are designated as d xy , d yz, d xz, dx 2 y 2 and d z2 The boundary surface diagrams ofThe 2 p orbitals are higher in energy than the 2 s orbital in multielectron atoms The same is true for the other quantum levels Look at the n =3 level for multielectron atoms in Figure 3 13 You see that the five 3 d orbitals are higher energy than the three 3 p orbitals, and that the 3 p orbitals are higher energy than the 3 s orbital We can adapt our skyscraper model to visualize the


Prelim Chemistry Electronic Configuration And Spdf Notation Art Of Smart



27 D Orbital Diagram Wiring Database
There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental) Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals In the n=1 shell you only find s orbitals, in the n=2 shell, you have s and p orbitals, in the n=3 shell, you have s, p and d orbitals and in the n=4The s, p, and d orbitals are quite familiar to anyone who has studied the electronic structure of atoms The forbitals, on the other hand, are not so familiar Interestingly, while the s, p, and d orbitals are presented as singular sets, there are two (2) sets in common usage for the forbitals cubic and general 1The s sublevel has one spherically shaped orbital, while the p sublevel has three dumbbell shaped orbitals The arrangement of electrons in orbitals can be depicted using either orbitals diagrams or electron configuration notation


Shapes Of The 4f Orbitals In 3d



Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube
In sp hybridization, the s orbital overlaps with only one p orbital Atoms that exhibit sp hybridization have sp orbitals that are linearly oriented;These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one node"s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!


Q Tbn And9gcqqfx6pzmsxdi2uw9vzetjpauxulquptk5uk642sgjdu4qcc5vw Usqp Cau



Wavefunctions Of Some S P D And F Orbitals Download Scientific Diagram
Energy Level Sublevel Number of atomic orbitals Total number of orbitals within the energy level 1 s 1 1 2 s p 1 3 4 3 s p d 1 3 5 9 4 s p d f 1 3 5 7 16 Look at how energy levels and electrons relate to each other Energy Level Total Number of Orbitals Total Number of Electrons 1 1 1 2 4 8 3 9 18 4 16 32 Electrons have _____ main PrinciplesEnergy Level Sublevel Number of atomic orbitals Total number of orbitals within the energy level 1 s 1 1 2 s p 1 3 4 3 s p d 1 3 5 9 4 s p d f 1 3 5 7 16 Look at how energy levels and electrons relate to each other Energy Level Total Number of Orbitals Total Number of Electrons 1 1 1 2 4 8 3 9 18 4 16 32 Electrons have _____ main PrinciplesIn a more realistic model, electrons move in atomic orbitals, or subshells There are four different orbital shapes s, p, d, and f Within each shell, the s subshell is at a lower energy than the p An orbital diagram is used to determine an atom's electron configuration There are guidelines for determining the electron configuration of an



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Shapes Of Orbitals Shape Of S Orbital P Orbital D Orbital F Orbital Node Angular Node Youtube
An illustration of the shape of the 3d orbitals Click the images to see the various 3d orbitals There are a total of five d orbitals and each orbital can hold two electrons The transition metal series is defined by the progressive filling of the 3d orbitalsThese five orbitals have the following m l values m l =0, ±1, ±2,Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals Orbital notation requires arrows denoting the spin of each electron Therefore the F electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5 The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectivelyThere are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental) Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals In the n=1 shell you only find s orbitals, in the n=2 shell, you have s and p orbitals, in the n=3 shell, you have s, p and d orbitals and in the n=4



Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic
This version of The Orbitron is a partial rewrite of the 02 version of The Orbitron It is not finished there are still some missing images, missing videos, errors in orbital names, many typos, incorrect labels, no hybrid orbitals, and no molecular orbitalsThis video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms n represents the energy leve



Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod
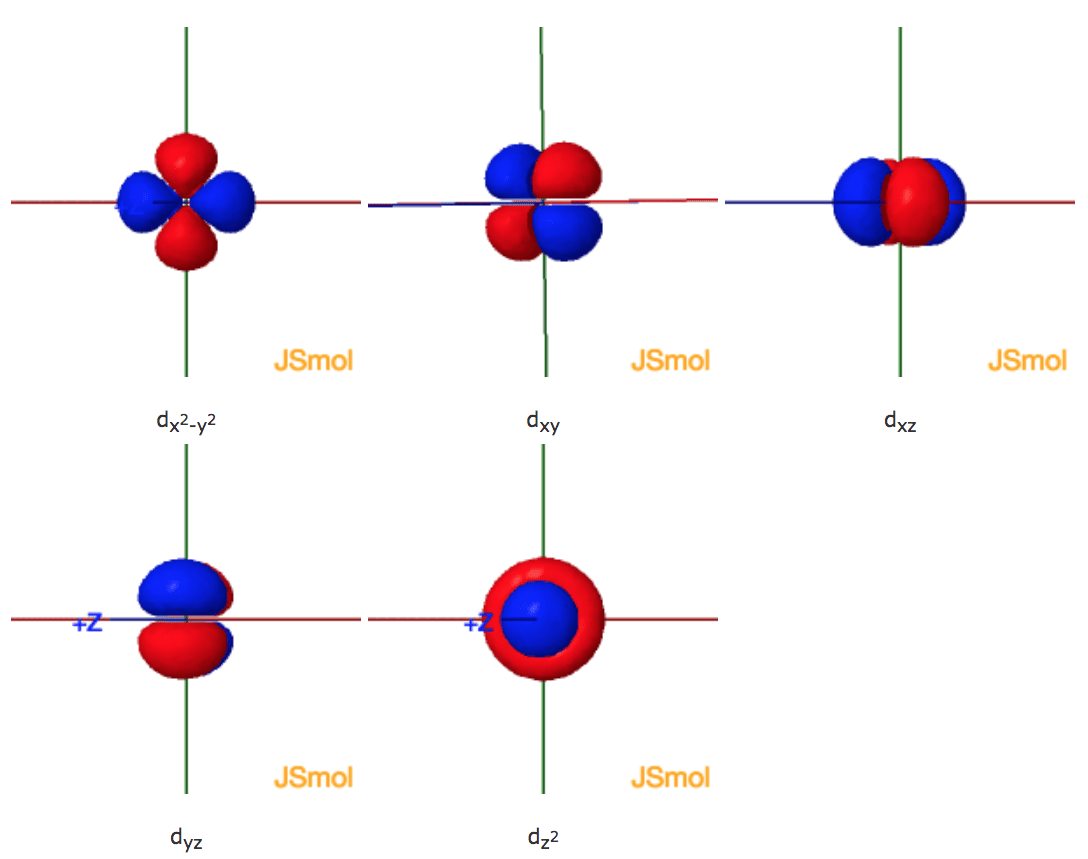


Shapes Of The 3d Orbitals In 3d


Http Pnhs Psd2 Org Documents Lcasey Pdf
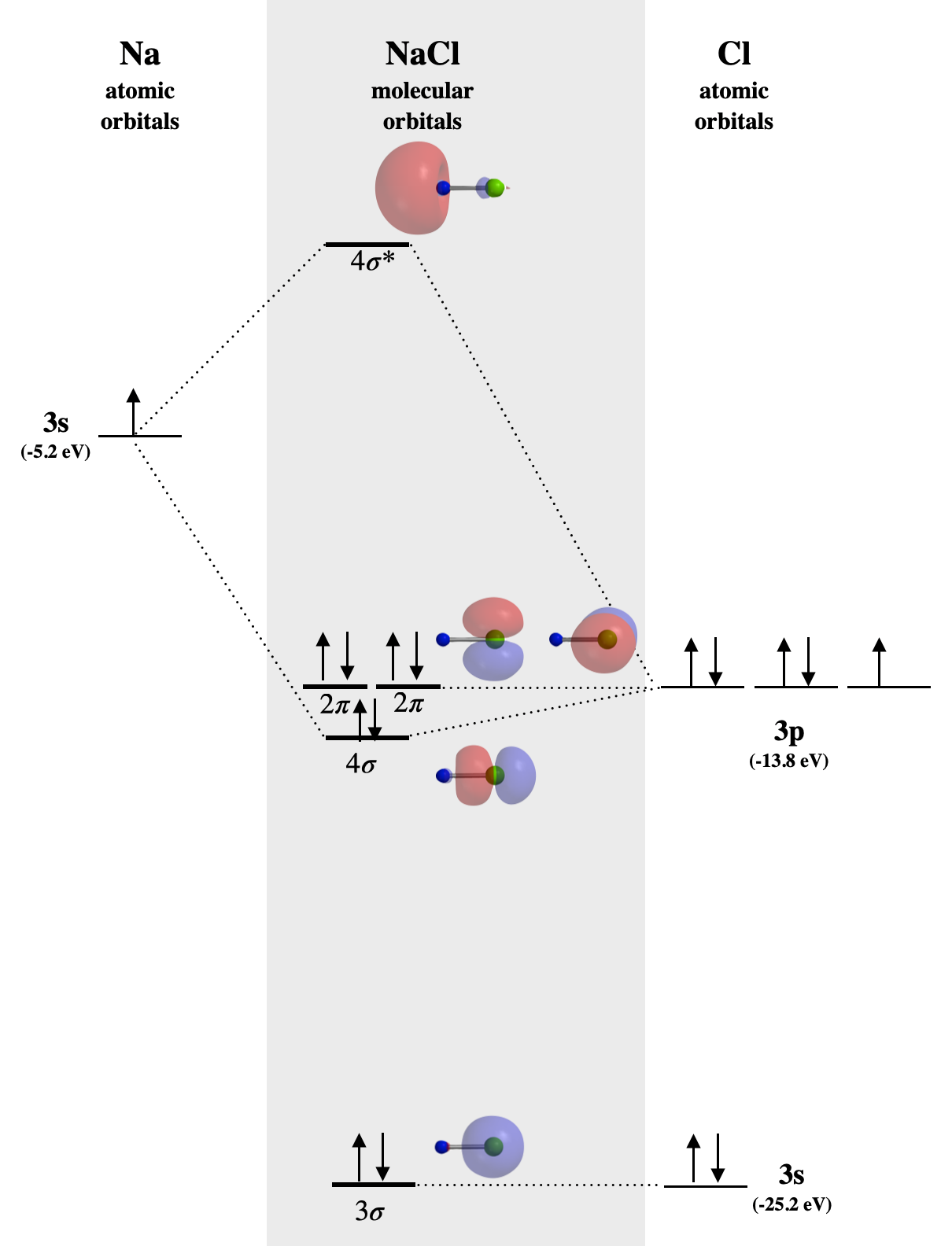


5 3 2 Ionic Compounds And Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
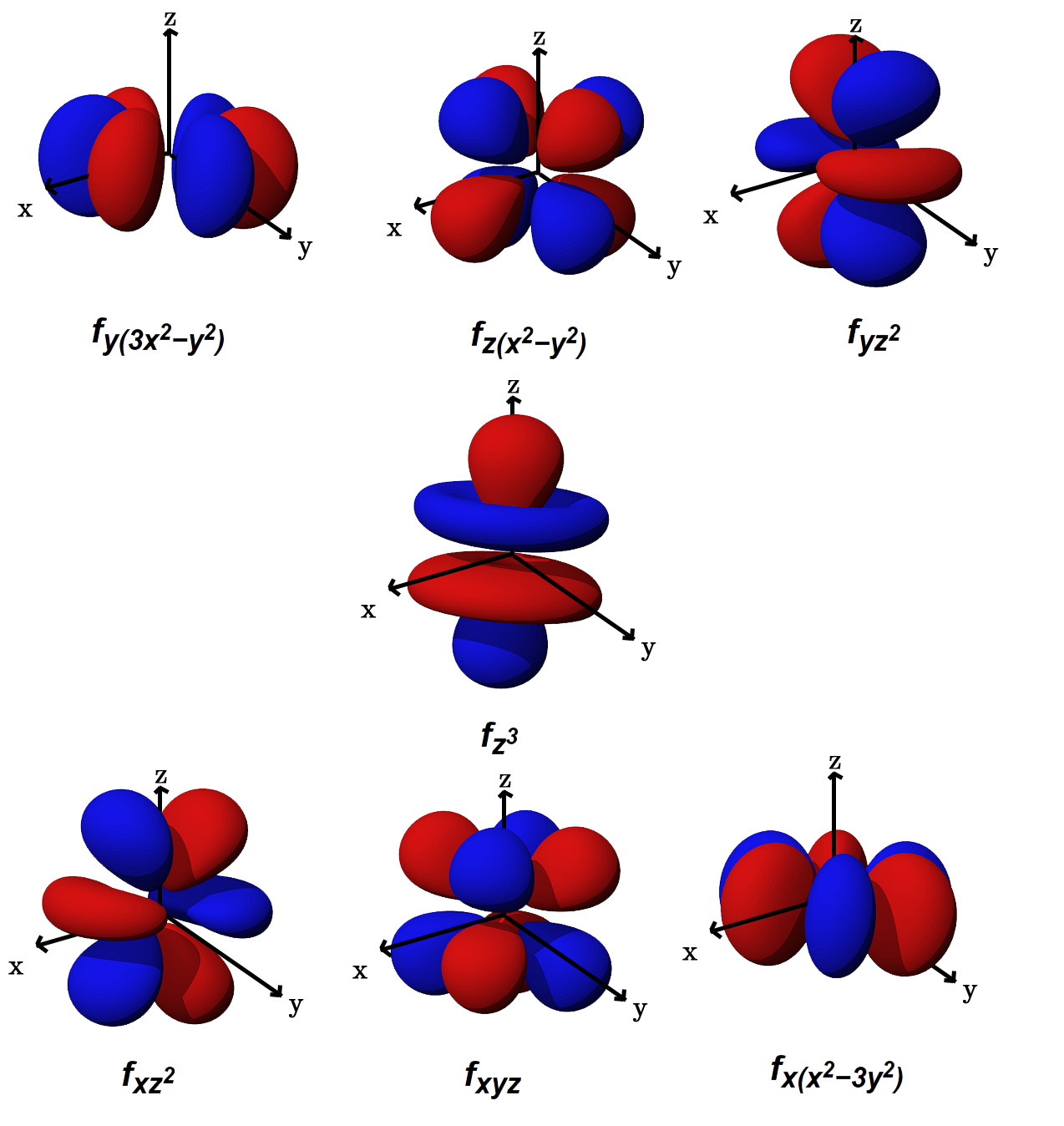


What Is The Shape Of F Orbital Example



Description Of The Splitting Of F Orbitals Of Tm 3 In O H And D 3 Download Scientific Diagram
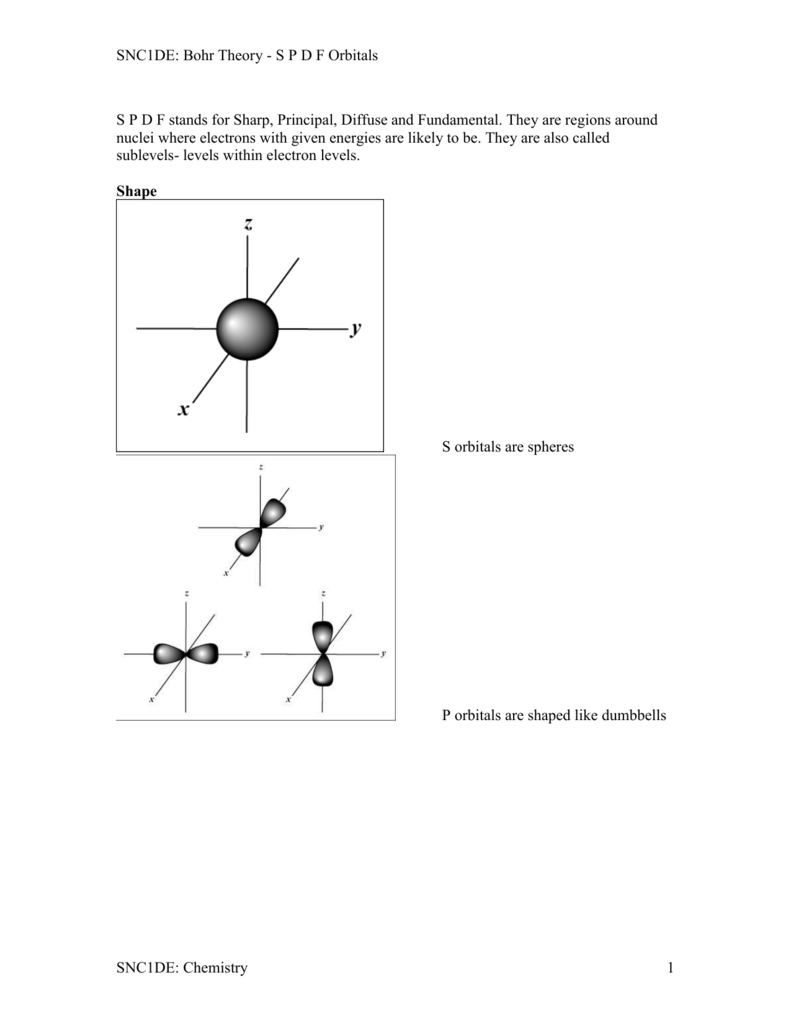


S P D F Orbitals



Electron Configuration Wikipedia


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



Mention The Shapes Of S P D F Orbitals Brainly In
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/antibonding-5b54ef9046e0fb005b6d11a9.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
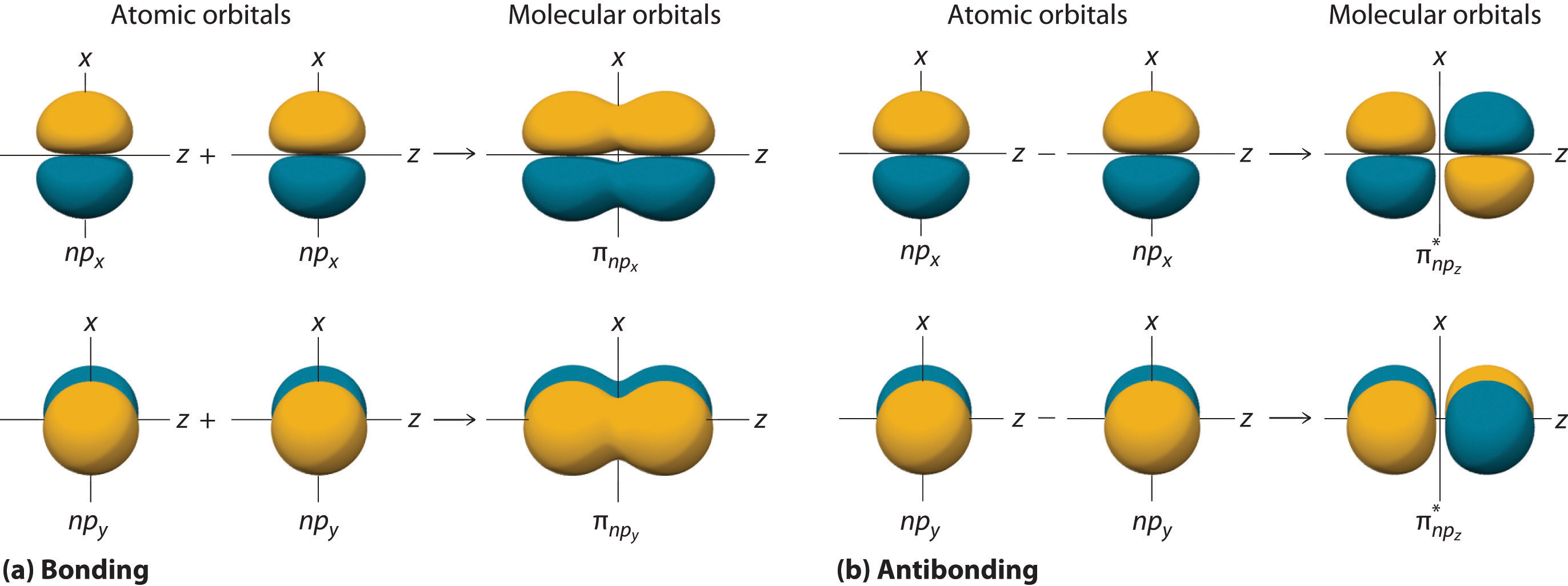


11 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts
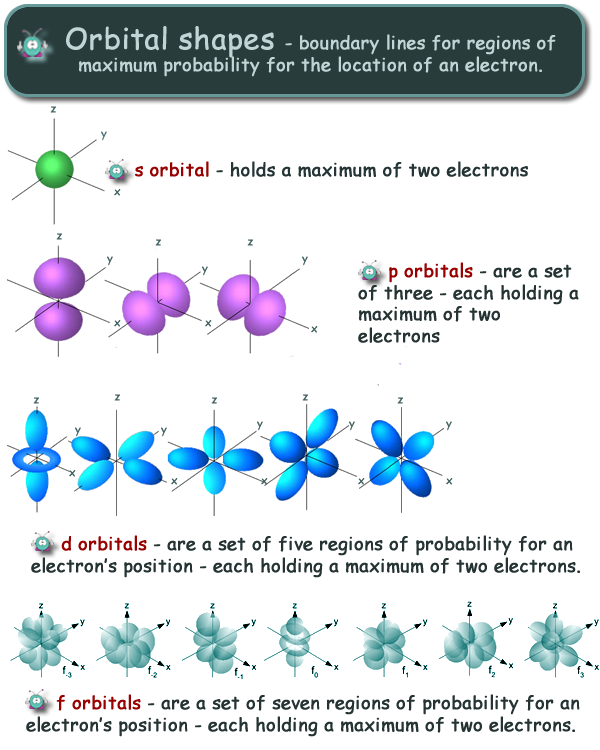


Physics Revision Gcse And A Level Physics Revision Cyberphysics The Revision Website


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital
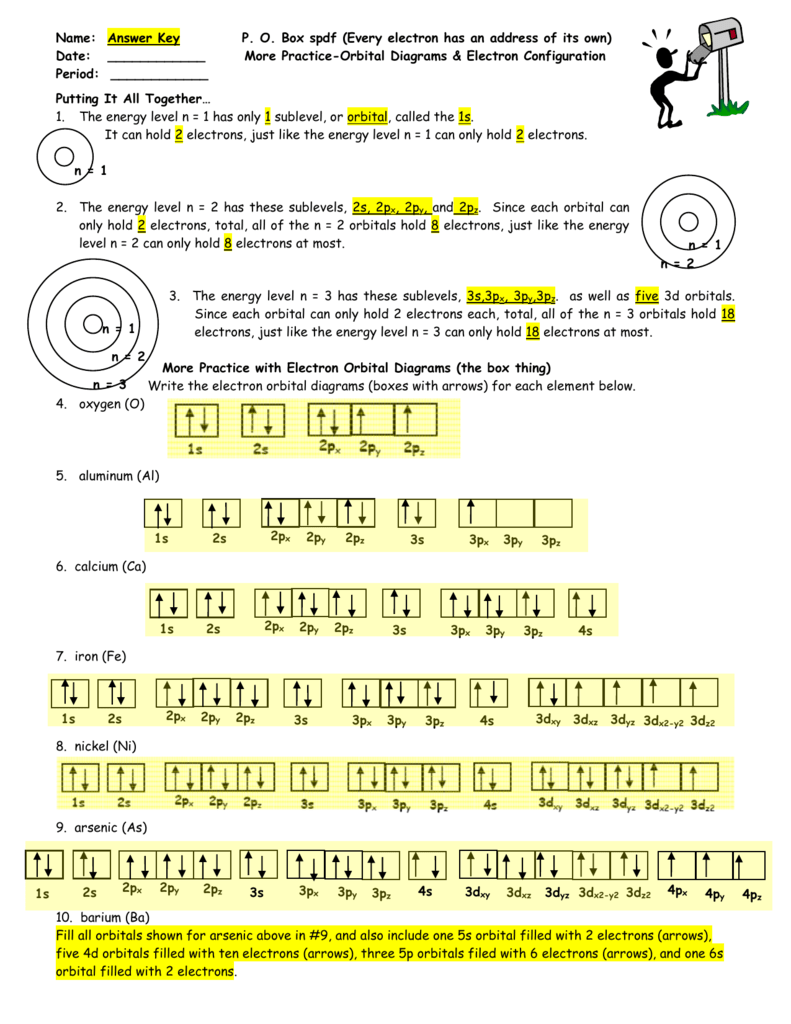


Po Box Spdf Worksheet Answer Key
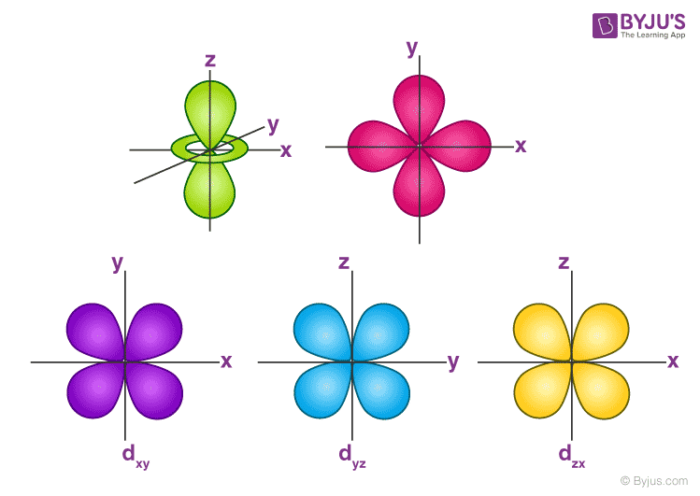


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube


Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates And Superpositions Magnetic Orbital Quantum Number Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download



Dublin Schools Lesson Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configurations


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Visualizing Electron Orbitals


What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora


Quantum Model And Spdf Orbitals Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau


What Is Names Of F Orbitals Quora



Orbital Diagrams Ppt Download


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


3


Co In M Zsm5



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry



Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configuration Basic Introduction Chemistry Practice Problems Youtube


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


How To Use Spdf Method For Electronic Configuration Chemistry Topperlearning Com 8ekub122
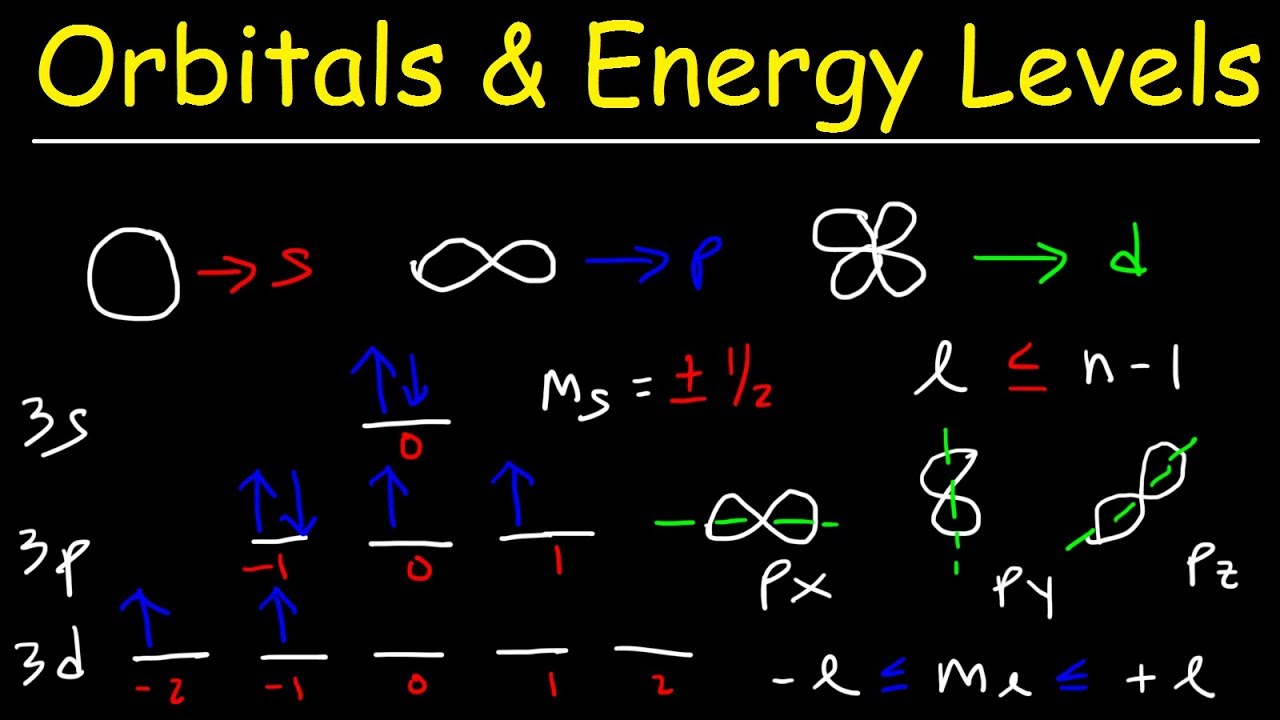


Orbitals Atomic Energy Levels Sublevels Explained Basic Introduction To Quantum Numbers Youtube



Orbitals Diagram For Spdf Quantum Numbers In High School Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Molecular Orbitals For Pf3



Dublin Schools Lesson Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configurations
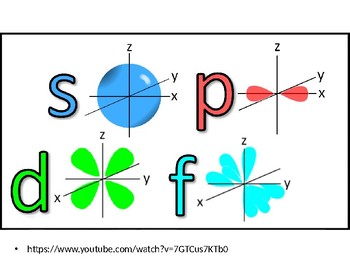


Shapes Of Orbitals By Science And The Big Ideas Tpt
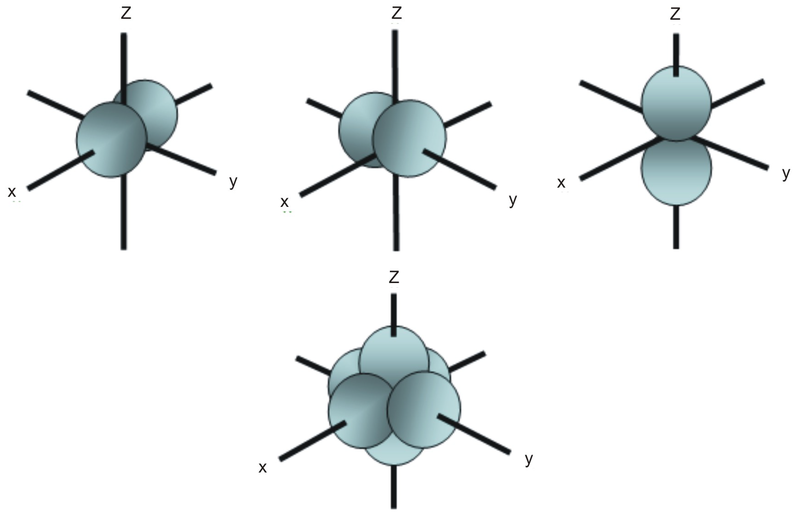


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


Atomic Orbitals
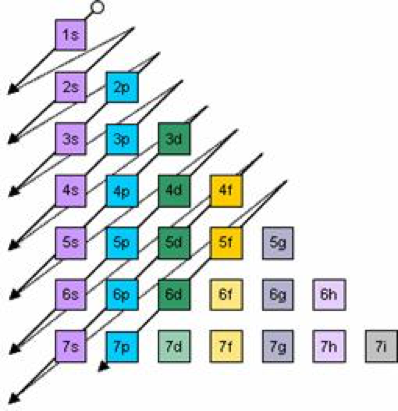


Electron Configurations Orbitals Energy Levels And Ionisation Energy Trends A Level Chemistry Revision Notes


Atomic Orbitals Definition Shapes Examples And Diagrams



Part 5 Shapes Of The Atomic Orbital S P D And F Orbital Atomic Structure Youtube


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


Electron Configuration Chart



F Bond Theory Molecular Orbitals Chemistry
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


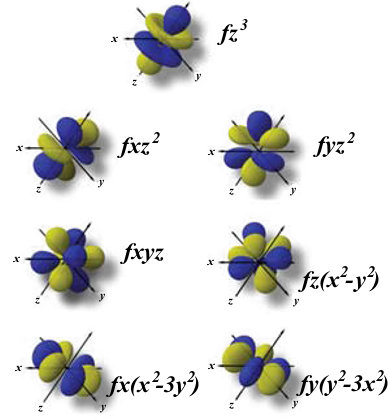
Ch150 Chapter 2 Atoms And Periodic Table Chemistry


Electron Configurations


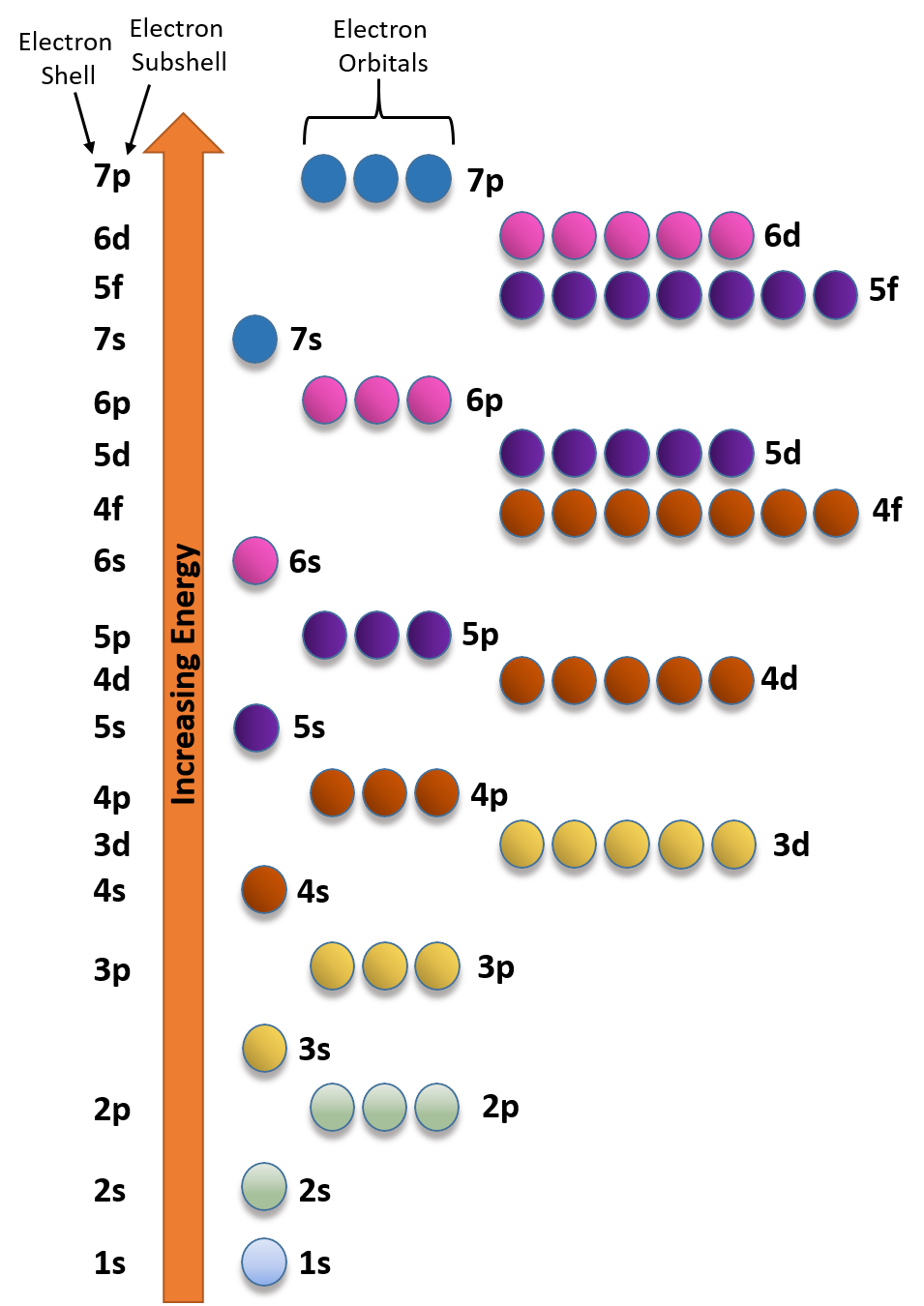
Electron Configuration Wyzant Resources


Shapes Of Orbitals S P D Shapes


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



Wavefunctions Of Some S P D And F Orbitals Download Scientific Diagram


Q Tbn And9gcqgp28lgnr6xcufpgiroedaenthgrys Oedjaqmrwowa3gfhdra Usqp Cau
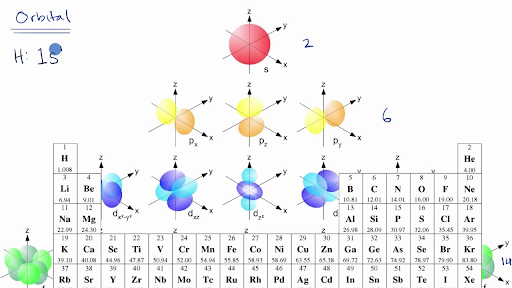


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy
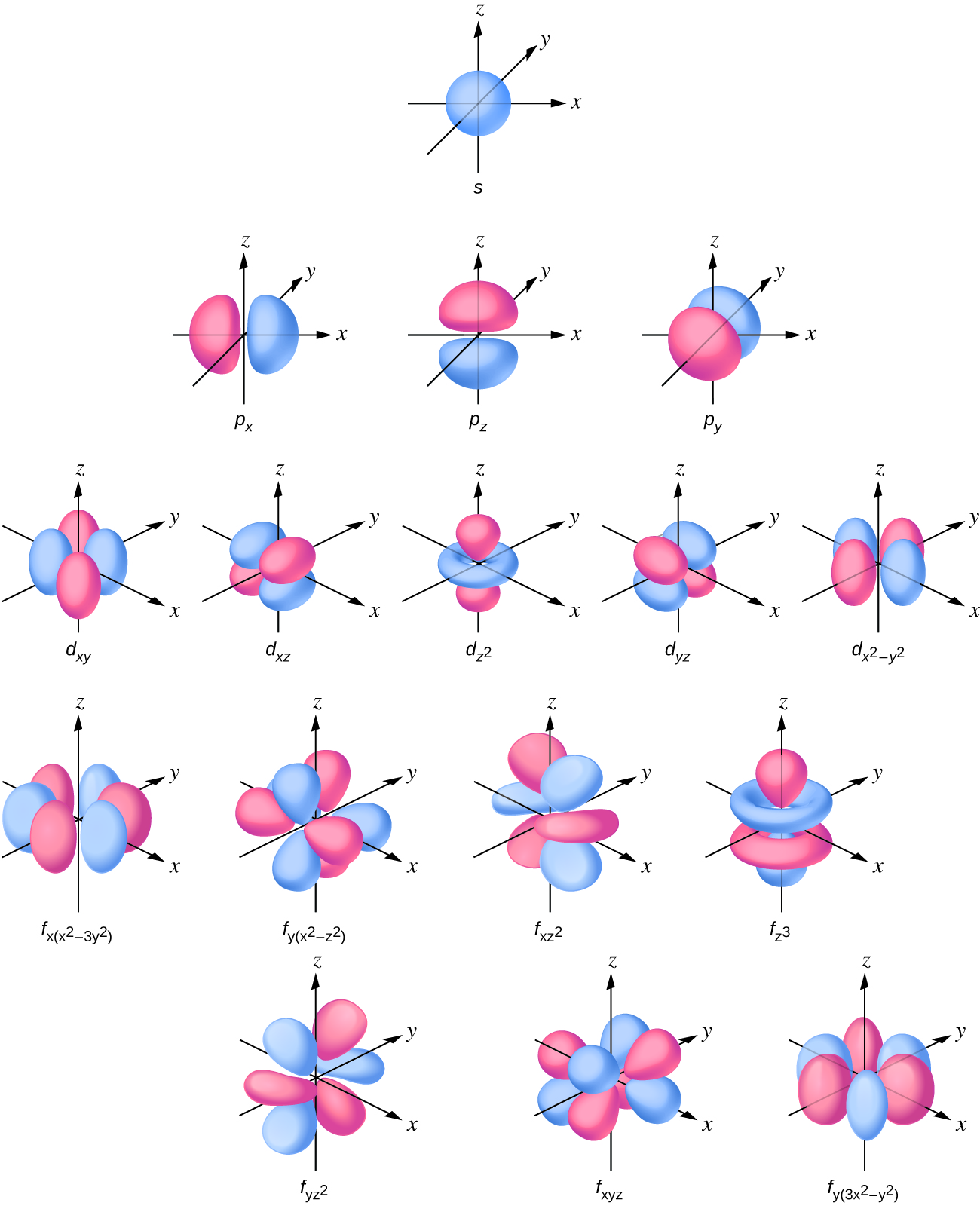


2 2 Atomic Orbitals And Quantum Numbers Chemistry Libretexts



Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
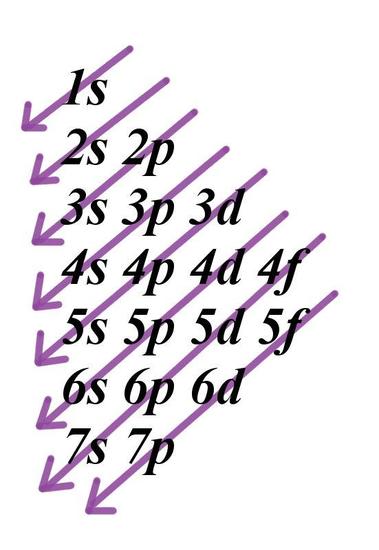


1 4 Electron Configurations Electronic Orbital Diagrams Review Chemistry Libretexts


Atomic Orbitals Chemistry Topics
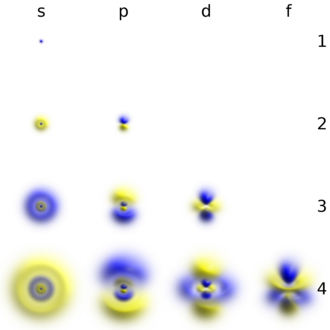


Electron Shell Wikipedia


An Atomic Model Our Present Model Of The Atom Is Based On The Concept Of Energy Levels For Electrons Within An Atom And On The Mathematical Interpretation Of Detailed Atomic Spectra The Requirements For Our Model Are Each Electron In A Particular Atom
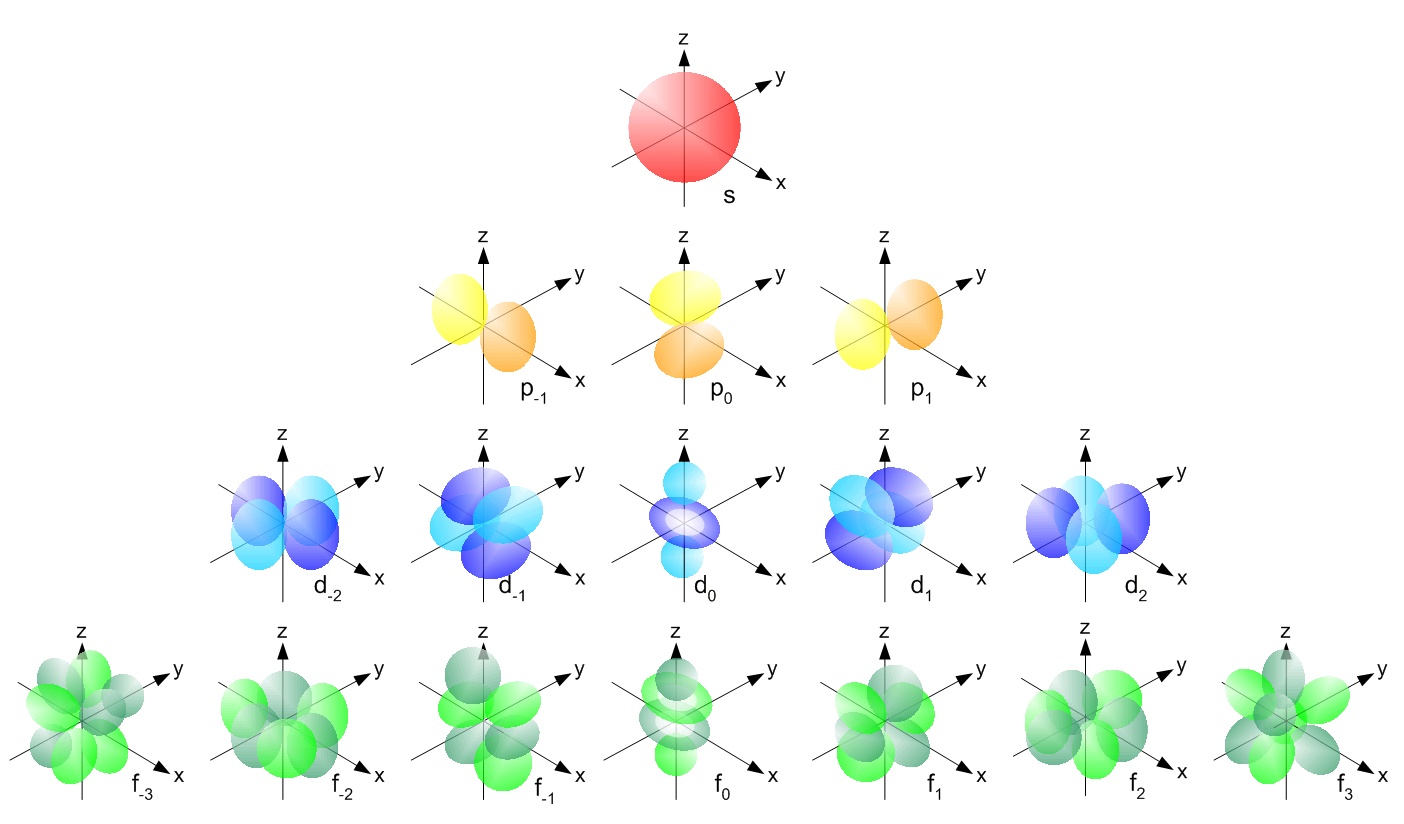


Electron Configuration
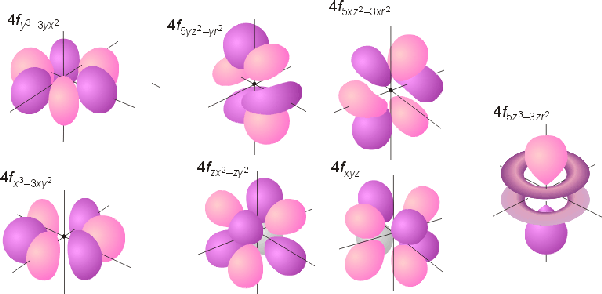


2a3 Orbitals


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model



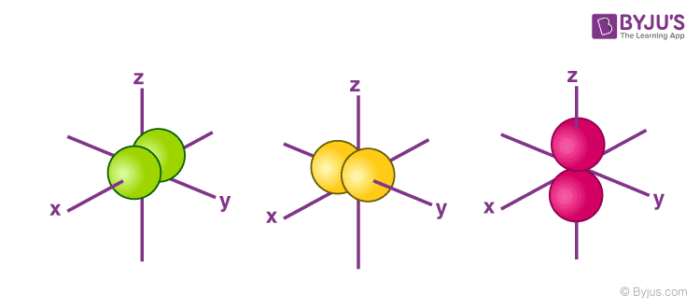
Degenerate Orbitals Explanation With Diagram Examples On Byju S


コメント
コメントを投稿